Hi, this is Lizzy from Dinosaw ( Not a Robot ). Which Machine ( model ) do you want? Please WhatsApp us now
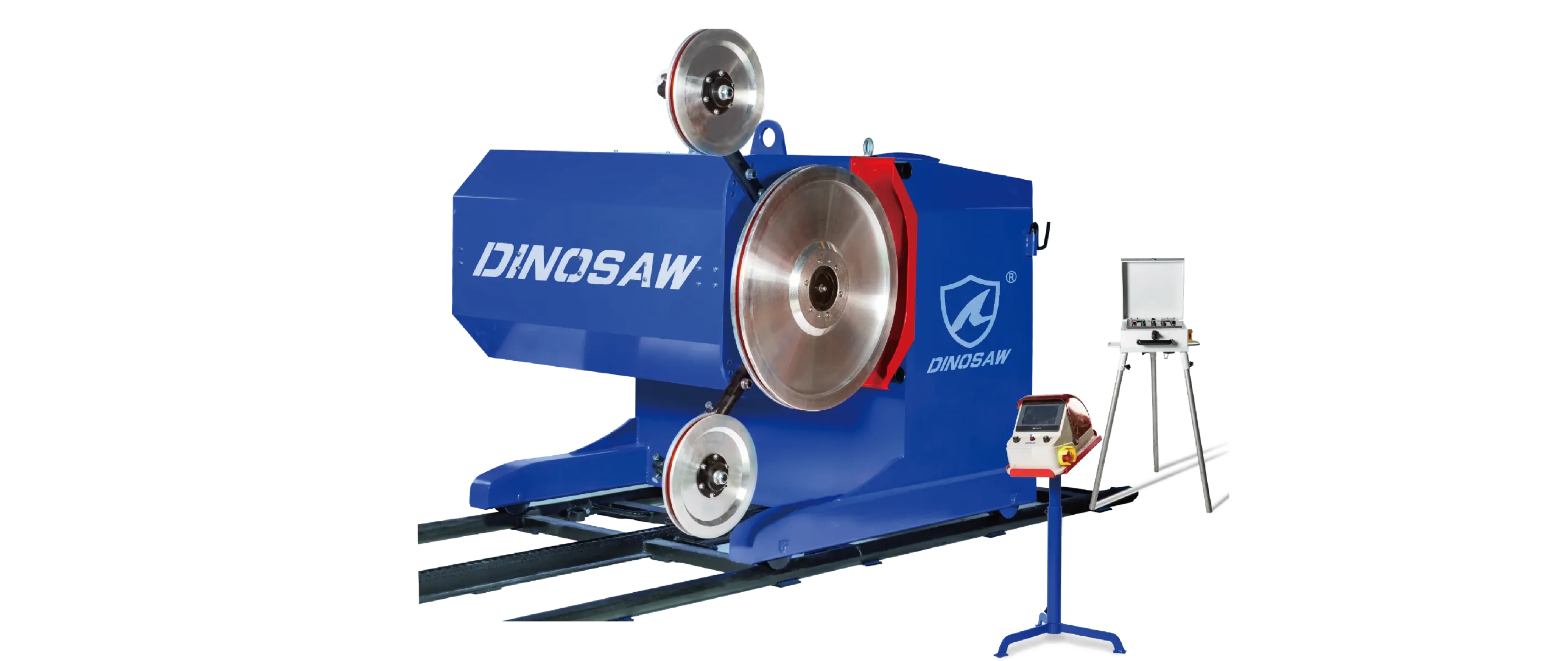
A detailed look at the technology behind CNC wire saw machines. Understand the principles, architecture, and core components like the tensioning system and guide wheels that deliver precision wire sawing.
How the system achieves precise wire sawing?
- Architecture: controller + drive + tensioning + guide wheels + axes.
- Diamond wire 3–15 mm; sintered/electroplated/brazed; match wire to material.
- Typical accuracy ±1 mm; start with the baseline settings, then test.
Have a technical question? Our engineers are ready to help you integrate our solution.
We will provide a technical definition, explore the system architecture, detail the core components with their operating parameters, and discuss common troubleshooting and compatibility topics to give you a comprehensive understanding of this powerful technology.
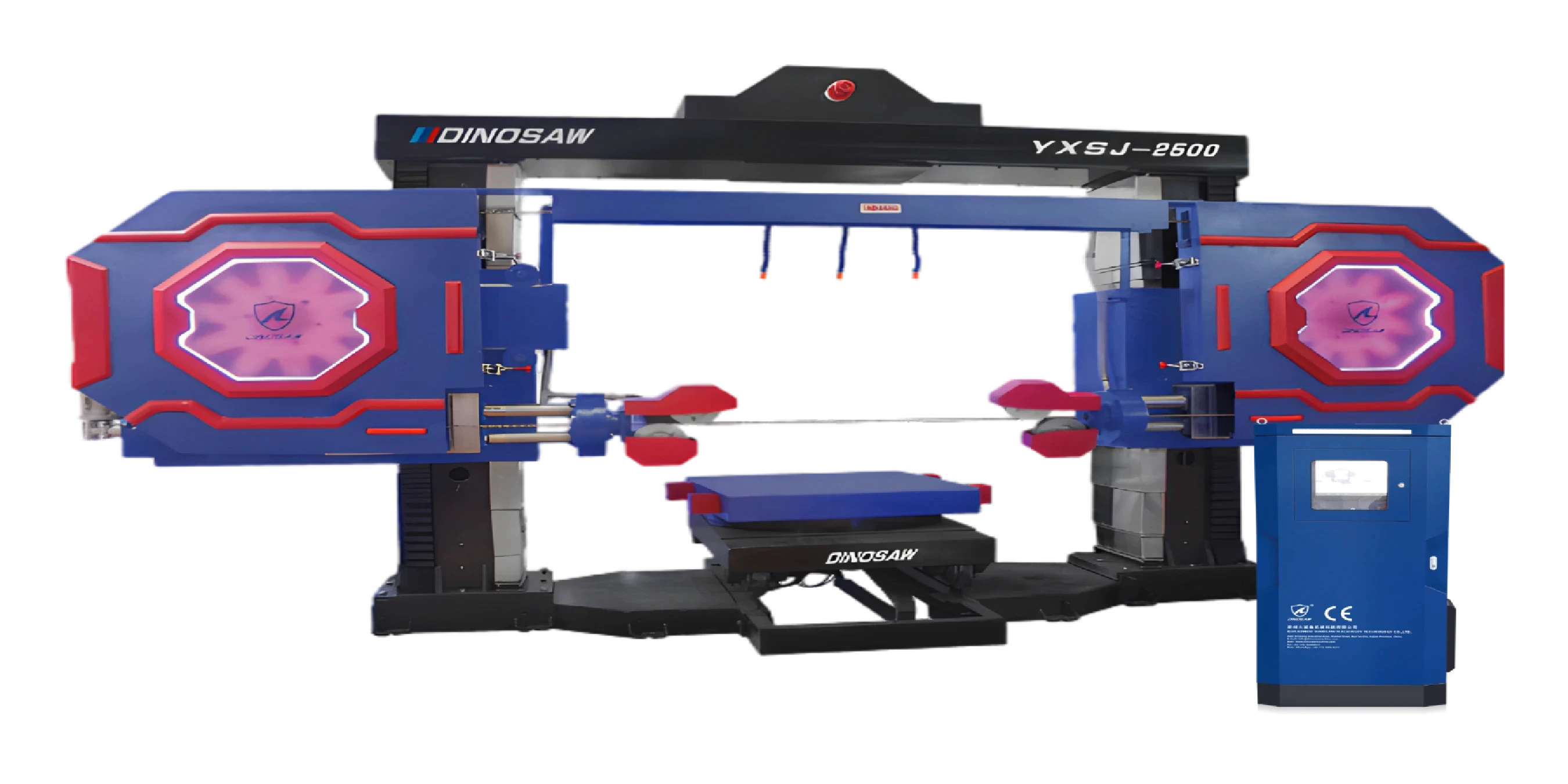

What is a CNC Diamond Wire Saw? A Technical Definition
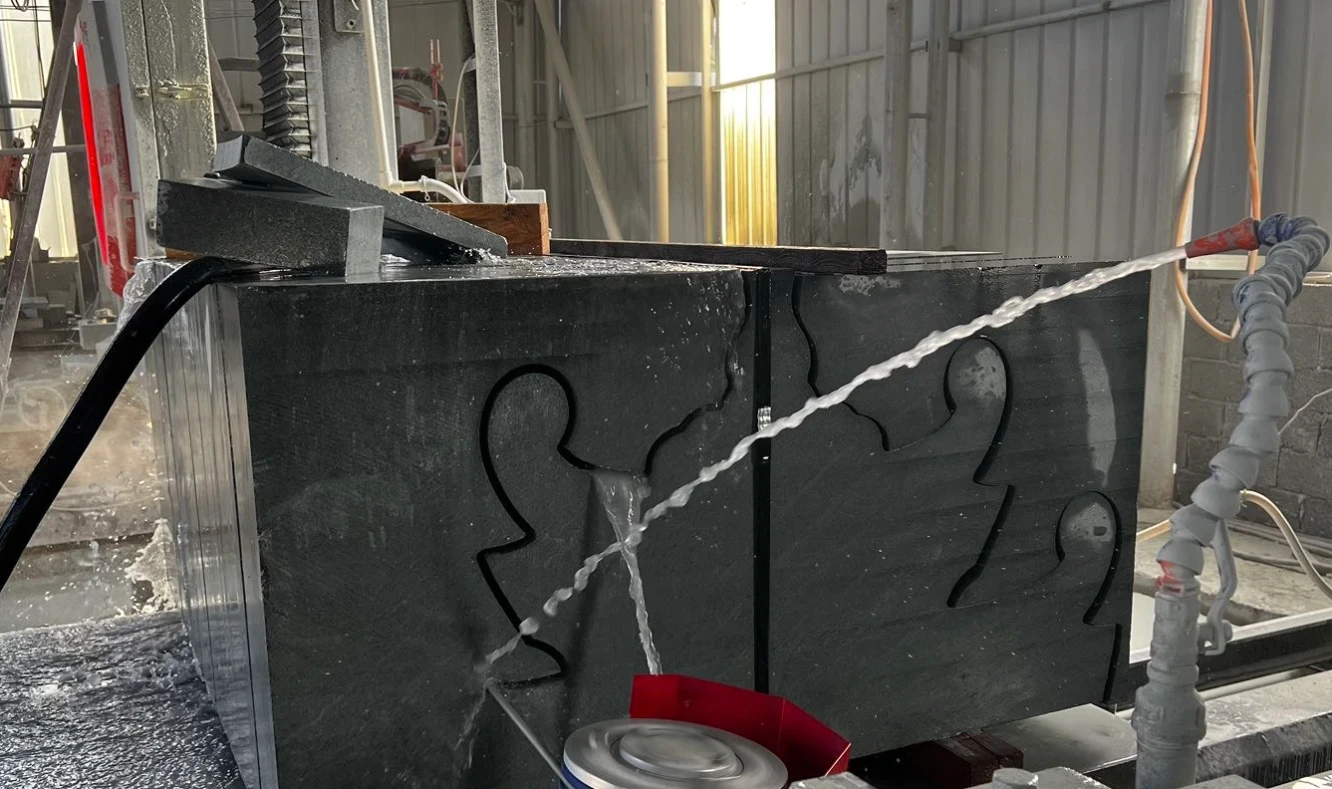
Technically, a CNC diamond wire saw machine is a computer-numerically controlled (CNC) system built for precision cutting of hard and brittle materials. Its cutting mechanism uses a continuous loop of high-tensile steel wire, typically 3 to 15 mm in diameter, which is impregnated or electroplated with diamond abrasives.
A motor and a series of guide wheels drive this diamond wire at high speeds-up to 25 m/s, according to manufacturer reports. This creates a linear abrasive action that removes material with minimal kerf loss and low thermal damage.
The CNC system precisely manipulates the wire's path in multiple axes (3, 4, or 5-axis). This control allows the machine to create complex contours, non-linear shapes, and intricate internal features that are impossible to achieve with traditional blade-based saws.
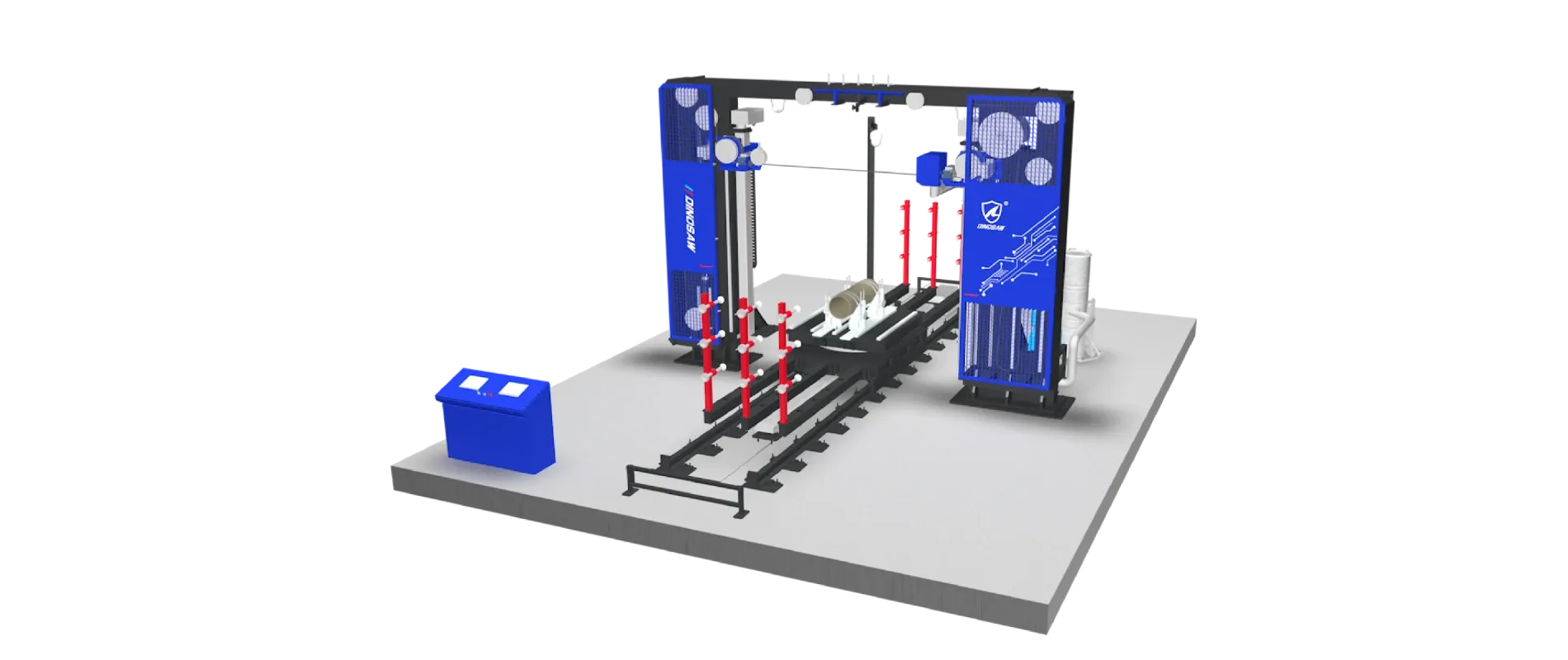
System Architecture & Working Principle of Wire Sawing Systems
The architecture of a cnc diamond cutting machine integrates mechanical, electrical, and software subsystems to achieve automated precision. The process begins with a CAD model, which is translated into G-code by CAM software. The CNC controller interprets this code to orchestrate the machine's movements.
Unable to load content.
The working principle is a combination of abrasion and controlled motion. The high-speed diamond wire acts as a flexible, continuous file. As it moves through the material, the diamond particles on its surface perform micro-grinding, chipping away material with high precision.
Coolant is essential to lubricate the wire, flush away debris (slurry), and dissipate heat to prevent wire damage and ensure a clean cut. For detailed operational steps, operators should consult the User Manual for CNC Wire Saw Machine.
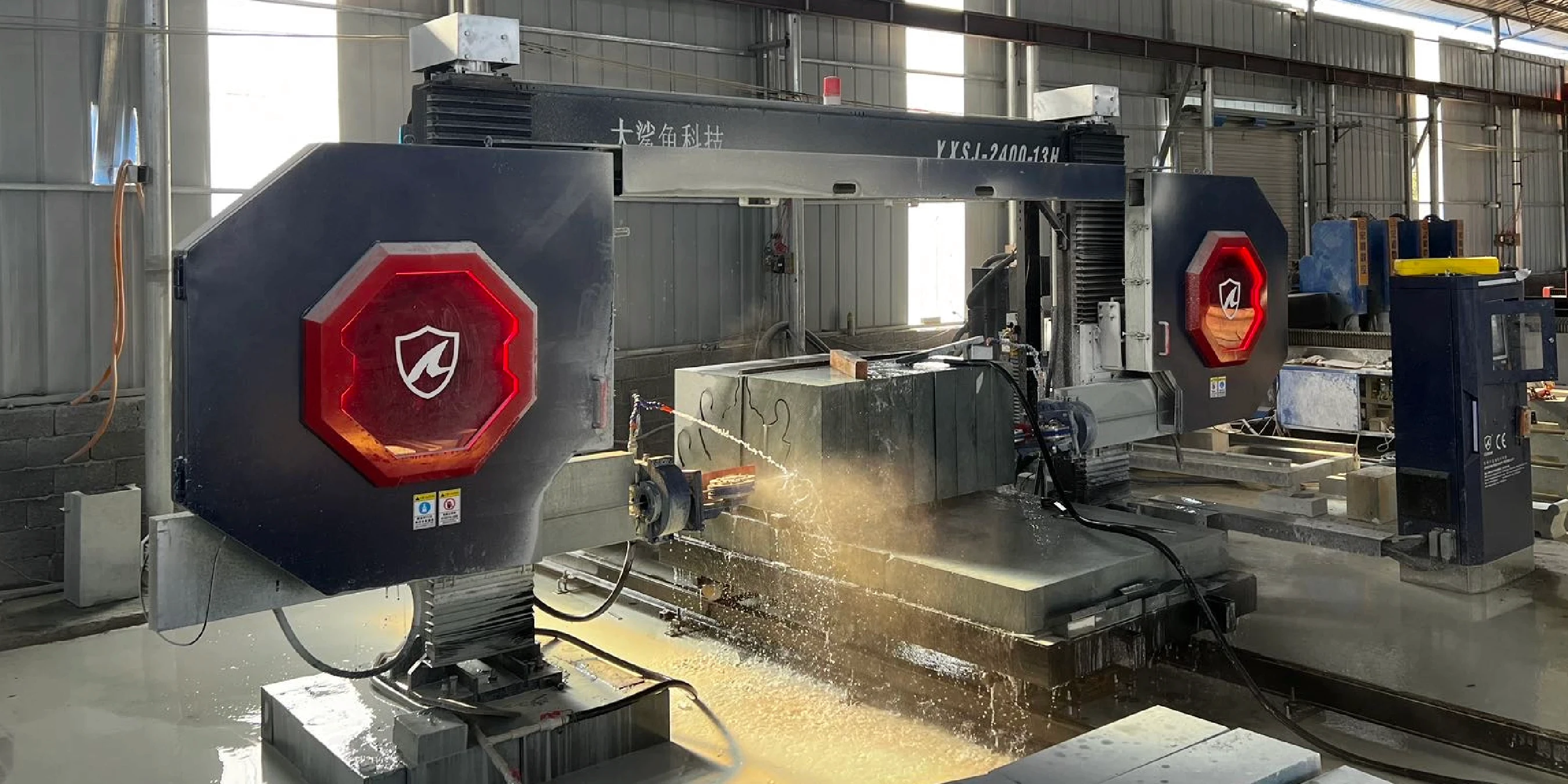

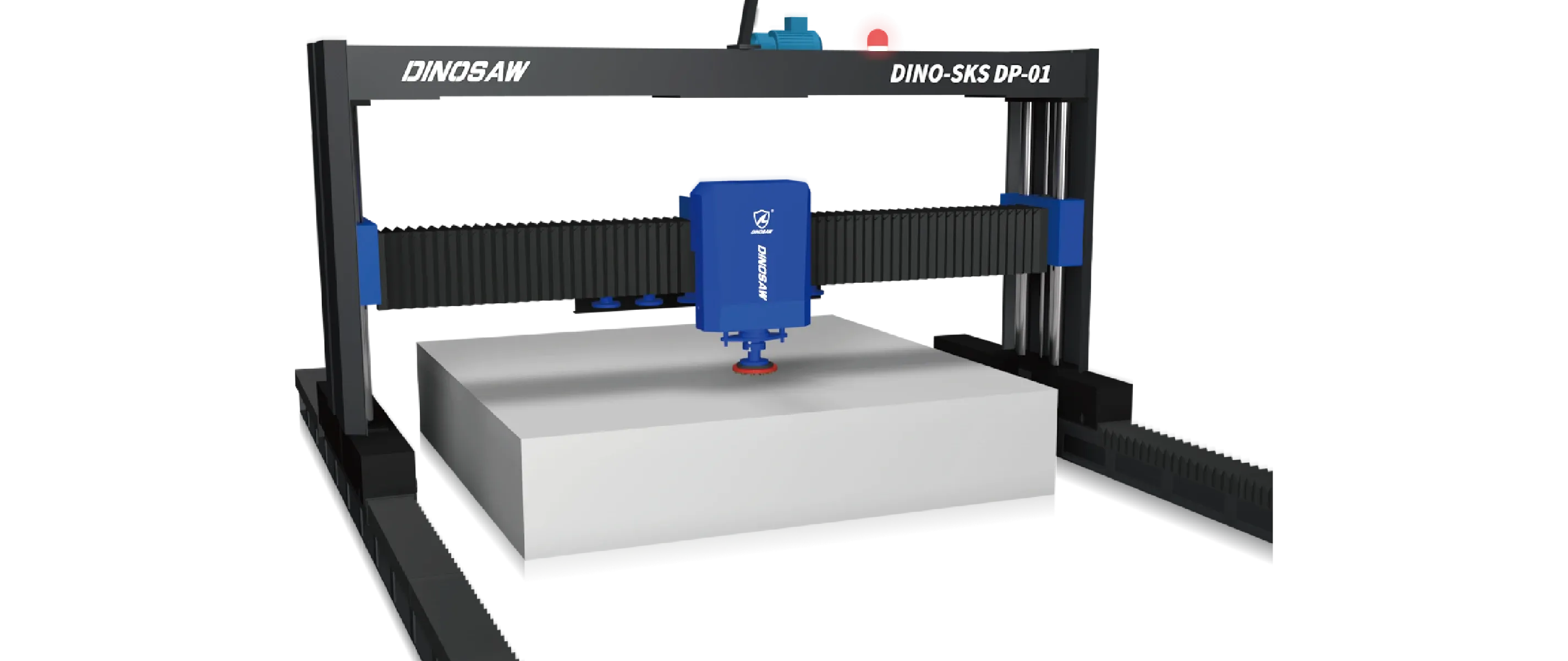
Core Components Breakdown: Tensioning System, Guide Wheels, and More
The performance of a CNC wire saw is determined by the quality and integration of its core components. Here are the key parts to examine:
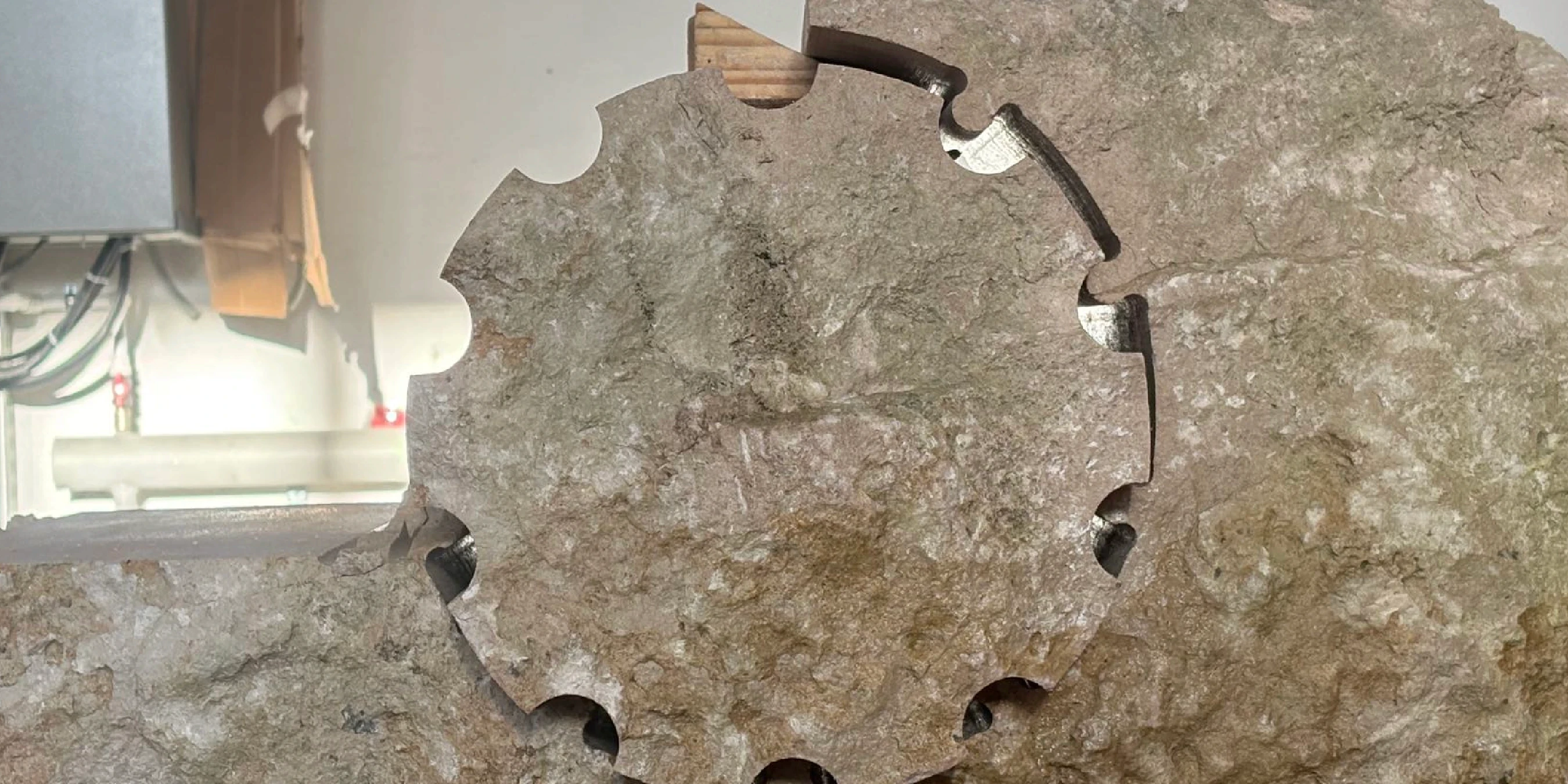
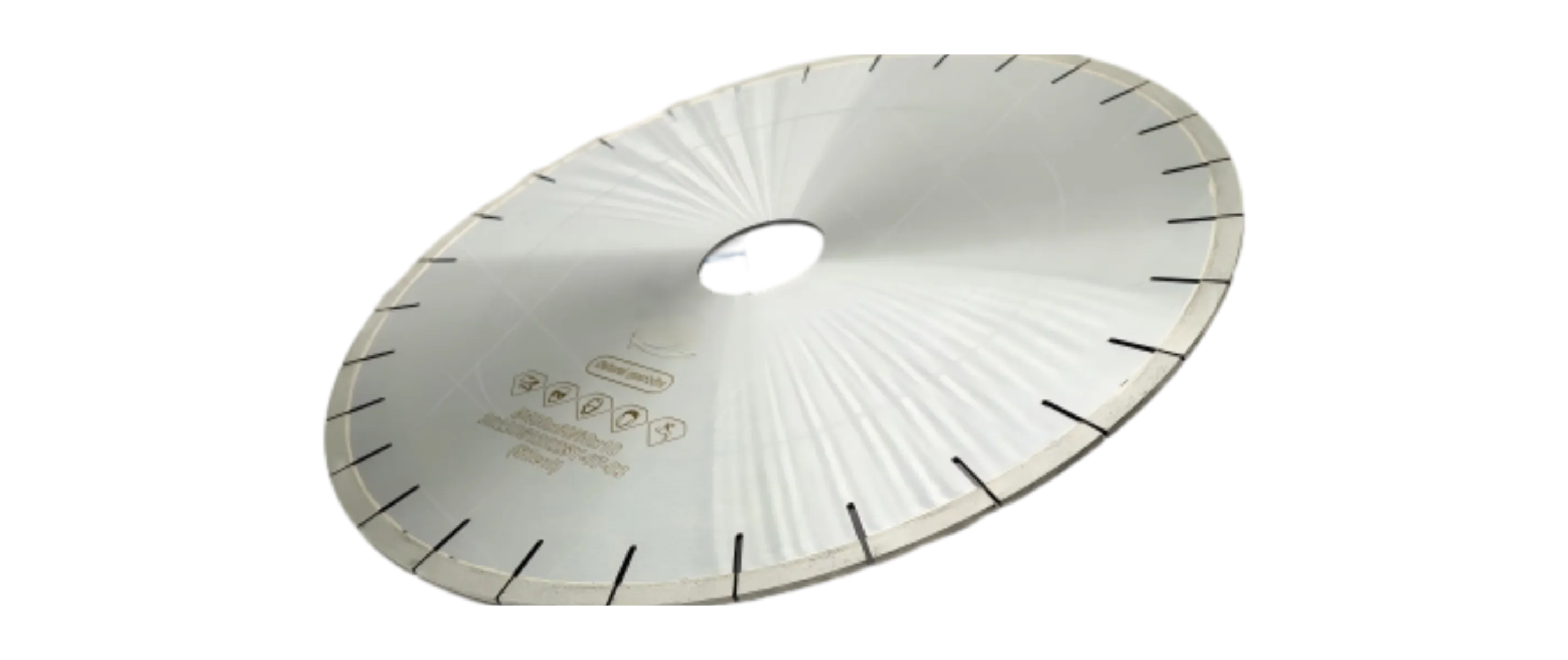
- Diamond Wire: The primary cutting tool. Available in various diameters (e.g., 3-15 mm) and diamond grit sizes. The choice depends on the material and desired surface finish. Wire life typically ranges from several hundred to over a thousand cutting meters depending on the application and material hardness. Processes include sintered, electroplated, and brazed; grit sizes and formulations vary. Use a material-specific diamond wire saw matched to your substrate, or cutting efficiency and finish may degrade. DINOSAW is a diamond wire sawing specialist with an in-house diamond tool factory. Tell us your material and requirements; we will match a wire to your job.
- Drive System: Consists of a high-power servo motor and a large flywheel. The motor provides the torque to achieve high wire speeds, while the flywheel ensures rotational inertia for stable, consistent wire velocity, even under varying loads. Standard main motor is ~15 kW; for very hard materials, consider ~22 kW.
- Wire Saw Tensioning System: Critical for preventing wire sag and breakage. This system typically uses a hydraulic or pneumatic cylinder to maintain constant tension (e.g., 100-250N) on the diamond wire. An integrated sensor provides feedback to the CNC controller to adjust tension automatically.
- Guide Wheels and Pulleys: These precision-machined wheels guide the wire from the flywheel to the workpiece. Their alignment is critical for cutting accuracy and preventing premature wire wear. Misalignment is a common cause of issues, as discussed in the guide wheel troubleshooting solution.
- CNC Controller and Software: The brain of the machine. It processes G-code, controls servo motors for multi-axis movement, manages wire speed and tension, and monitors safety sensors. Modern systems feature intuitive graphical interfaces and support standard file formats like DXF from common CAD/CAM software.
- Machine Frame and Worktable: A heavy, rigid, stress-relieved steel frame is essential to absorb vibrations and ensure long-term cutting accuracy. The worktable, often made of cast iron or steel, must be perfectly flat and robust enough to support heavy workpieces.

Common Failures & Mitigation (CNC Wire Saw Troubleshooting)
| Failure/Symptom | Common Causes | Mitigation/Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent Wire Breakage | Incorrect tension; Worn guide wheels; Excessive cutting speed; Debris in the cutting path. | Calibrate tensioning system. Inspect and replace worn wheels. Reduce cutting speed. Improve coolant flushing. |
| Uneven Cuts or Poor Accuracy | Wire sag (low tension); Misaligned guide wheels; Loose workpiece fixture; Vibration in the frame. | Increase wire tension within spec. Realign guide wheels. Securely clamp the workpiece. Check machine leveling and foundation. |
| Machine Alarms (e.g., Tension Fault) | Hydraulic/pneumatic pressure loss; Faulty sensor; Wire slippage on the flywheel. | Check fluid/air lines and pressure. Test sensor functionality. Clean flywheel and wire of excess coolant/slurry. |
Most failures can be prevented with a diligent maintenance schedule. For a complete guide, refer to our article on how to maintain a wire saw machine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cutting accuracy of a CNC wire saw?
The cutting accuracy of a properly calibrated CNC wire saw is one of its main advantages, allowing for high-precision work on demanding projects. A well-maintained machine can typically achieve a cutting accuracy within ±1 mm, which is crucial for applications requiring tight tolerances.
However, the final achievable accuracy depends on several factors, including the machine's structural rigidity, workpiece size, material properties, and wire condition. For projects requiring the highest precision, using a new suitable wire and a slower feed rate is recommended.
What causes the diamond wire to break?
Diamond wire breakage is a common operational issue that can halt production, but it is almost always preventable as it usually stems from incorrect machine parameters or worn components.
The most frequent causes include incorrect wire tension (either too high or too low), an excessive feed rate for the material, worn-out guide wheels creating excess friction, or simply running the wire past its recommended operational lifespan. Effective prevention requires a combination of proactive maintenance and strict adherence to correct operational parameters for each job.
How do you choose the right diamond wire for a material?
Selecting the right diamond wire requires balancing cutting speed with the desired surface finish for a specific material. The choice primarily involves the diamond grit size, wire diameter, and bond type.
For hard, dense materials like granite, a wire with a coarser and more aggressive diamond grit (e.g., 40/50 mesh) is generally chosen to maximize cutting efficiency. Conversely, for achieving a finer finish on delicate materials like marble, a wire with finer diamond particles (e.g., 60/70 mesh) is more appropriate as it reduces chipping. The ideal wire specification will vary depending on your specific machine capabilities and the material being cut. Always consult DINOSAW for guidance tailored to your equipment.
Can the machine be integrated with our existing CAD/CAM software?
Yes, most modern CNC wire saw controllers are designed for seamless integration with industry-standard CAD/CAM software, allowing for a smooth workflow from design to finished product.
Typically, these machines accept G-code files generated from popular programs like Fusion 360, Mastercam, or specialized stone-cutting software, and they support common file imports like .dxf and .step.
What is the typical power consumption?
The power consumption of a CNC wire saw is a key factor in calculating its total cost of ownership, and it is primarily driven by the main motor's power rating. For typical models, a 15 kW motor is standard. For very hard materials, an upgrade to a 22 kW motor should be considered. Power consumption peaks during machine startup and when cutting through particularly dense or thick materials.

















 English
English

